# T[vuerouter]
# vue3+vue-router@4版本写法

# vue路由重定向redirect
如何可以让路径默认跳到到首页, 并且<router-view>渲染首页组件呢?
{
path: "/",
redirect: "/home"
},
{
path: "/home",
name: "home",
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "home-chunk" */"../pages/Home.vue"),
meta: {
name: "why"
},
children: [
{
path: "",
redirect: "/home/message"
},
{
path: "message",
component: () => import("../pages/HomeMessage.vue")
}
]
},
# vue 嵌套路由
- active-class属性:设置激活a元素后应用的class,默认是router-link-active
- exact-active-class属性:链接精准激活时,应用于渲染的
<a>的 class,默认是router-link-exact-active;
{
path: "/home",
name: "home",
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "home-chunk" */"../pages/Home.vue"),
meta: {
name: "why"
},
children: [
{
path: "",
redirect: "/home/message"//如果重定向的话,要注意完整路径
},
{
path: "message",//不需要加/开头
component: () => import("../pages/HomeMessage.vue")
}
]
},
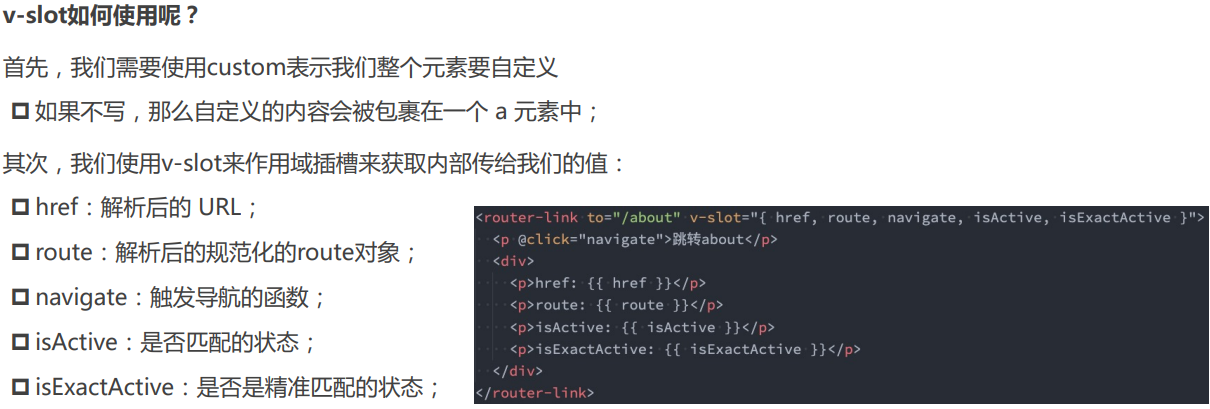
# router-link
在vue-router3.x的时候,router-link有一个tag属性,可以决定router-link到底渲染成什么元素:
- 但是在vue-router4.x开始,该属性被移除了;
- 而提供了更加具有灵活性的v-slot的方式来定制渲染的内容;
# vue编程式路由
// router.go(-1)
// router.forward()
// router.back()
//router.push(xxx)
router.replace(xxx)
# router-view
router-view也提供给我们一个插槽,可以用于 <transition> 和 <keep-alive> 组件来包裹你的路由组件:
- Component:要渲染的组件;
- route:解析出的标准化路由对象;
<router-view v-slot="props">
<!-- <transition name="why"> -->
<keep-alive>
<component :is="props.Component"></component>
</keep-alive>
<!-- </transition> -->
</router-view>
# Hash 模式
www.test.com/#/ 就是 Hash URL,当 # 后面的哈希值发生变化时,可以通过 hashchange 事件来监听到 URL 的变化,从而进行跳转页面,并且无论哈希值如何变化,服务端接收到的 URL 请求永远是 www.test.com。
window.addEventListener('hashchange', () => {
// ... 具体逻辑
})
Hash 模式相对来说更简单,并且兼容性也更好,页面不刷新,会有前进后退操作。
# History 模式
History 模式是 H5 新推出的功能,主要使用 history.pushState 和 history.replaceState 改变 URL。
通过 History 模式改变 URL 同样不会引起页面的刷新,只会更新浏览器的历史记录。
// 新增历史记录
history.pushState(stateObject, title, URL)
// 替换当前历史记录
history.replaceState(stateObject, title, URL)
当用户做出浏览器动作时,比如点击后退按钮时会触发 popState 事件
window.addEventListener('popstate', e => {
// e.state 就是 pushState(stateObject) 中的 stateObject
console.log(e.state)
})
# 两种模式对比
- Hash 模式只可以更改 # 后面的内容,History 模式可以通过 API 设置任意的同源 URL
- History 模式可以通过 API 添加任意类型的数据到历史记录中,Hash 模式只能更改哈希值,也就是字符串
- Hash 模式无需后端配置,兼容性好。History 模式在用户手动输入地址或者刷新页面的时候会发起 URL 请求,后端需要配置 index.html 页面用于匹配不到静态资源的时候
1.安装 vue-router
cnpm i vue-router -save
2.在src下创建router目录,目录下方index.js进行路由配置 3.配置index.js
//引入vue和vue-router及所有路由组件
import Vue from 'vue'
import Router from 'vue-router'
import Login from '../components/Login'
import Index from '../components/Index'
import Work from '../components/Work'
import Linkman from '../components/Linkman'
import Qq from '../components/Qq'
//使用router
Vue.use(Router)
//注意参数是routes
export default new Router({
routes: [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Login',
component: Login
},
{
path: '/qq',
name: 'Qq',
component:Qq
},
{
path: '/index',
name: 'Index',
component: Index,
//有子路由的配置
children:[
{
path: '',
name: 'Work',
component:Work
},
{
path: 'linkman',
name: 'Linkman',
component:Linkman
}
]
}
]
})
- mainjs挂载路由
import router from './router'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
- 跳转路由
import router from "../router";
router.push(`/index`)
query一般要用 path 来引入,params一般要用 name 来引入,接收参数都是类似的,分别是 this.$route.query.name和 this.$route.params.name
# params模式
//params传参 使用name
this.$router.push({
name:'second',
params: {
id:'20180822',
name: 'query'
}
})
//params接收参数
this.id = this.$route.params.id ;
this.name = this.$route.params.name ;
//路由
{
path: '/second/:id/:name',
name: 'second',
component: () => import('@/view/second')
}
# query模式
import router from "../router";
router.push(`/meetingdetail?id=${v}`)
//axiosget请求中,用的params其实和url写在?后的效果一致,其实这和vue-router无关系!!!
let that=this;
Indicator.open()
this.$axios.get('/conference/selectDetailCon',{
params:{
id:that.$route.query.id
}
})
//传参:
this.$router.push({
path:'/xxx',
query:{
id:id
}
})
//接收参数:
this.$route.query.id
注意
获取参数时,注意是$route!!!!
- $router为VueRouter实例,想要导航到不同URL,则使用$router.push方法
- $route为当前router跳转对象,里面可以获取name、path、query、params等
# vue动态路由匹配和name与path传参
- 动态路由:path中添加了动态参数
{
path: '/about/:have',
name: 'About11',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
},
- 跳转时可以使用push name的方法,也可以使用push path的方法
- 使用path传参
this.$router.push('about/3')
// /#/about/3 浏览器可以看到3
- 使用name传参
this.$router.push({
name:'About11',
params:{
have:1000,
hello:30000
}
})
// /#/about/1000 浏览器只能看到hava的1000,name无法查看
// 在About.vue中可以获取$route.params => {have: 1000, hello: 30000}
// hava作为动态参数了
- 如果不是动态路由,使用path传递params的参数,字符串方法会失败,对象方法会成功,但是params会是个空对象,使用name对象方法能成功,且所有参数都已查到
{
path: '/testpath',
name: 'Test',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "test" */ '../views/Test.vue')
}
this.$router.push({
path:'/testpath',
params:{
id:2
},
query:{
id:1000
}
})
//只能打印出1000
this.$router.push("/testpath/2?id=300")
//匹配不到路由页面
this.$router.push({
name:'Test',
params:{
id:2
},
query:{
id:1000
}
})
// {id: 2}
// {id: 1000}
# vue-router 404配置
vue-router@4版本,可编写一个动态路由用于匹配所有的页面
{
path: "/:pathMatch(.*)",//固定写法
component: () => import("../pages/NotFound.vue")
}
- 通过 $route.params.pathMatch获取到传入的参数:/aa/bb/cc
- /:pathMatch(.*)* 后面又加了一个 *,参数被解析陈数组['aa','bb','cc']
新路由 删除 *(加注星标或捕获全部)匹配方式,新增:/:pathMatch(.*) *;
//通配符的使用
{
path: '/user-*',
component:test
},
{
path: '/*',
component:notFound
}
//{ path: '*' // 会匹配所有路径 } { path: '/user-*' // 会匹配以 `/user-` 开头的任意路径 }
# 路由的守卫
- 全局守卫
- 独享守卫
- 组件内守卫
next
vue3不推荐在beforeEach使用next参数!(暂时保留)
全局的前置守卫beforeEach是在导航触发时会被回调的,它有两个参数:
- to:即将进入的路由Route对象;
- from:即将离开的路由Route对象;
它有返回值:
- false:取消当前导航;
- 不返回或者undefined:进行默认导航;
- 返回一个路由地址:
- 可以是一个string类型的路径;
- 可以是一个对象,对象中包含path、query、params等信息;
- 可选的第三个参数:next
# main.js中设置全局守卫全局守卫
作用:登录校验跳转等
回调函数中的参数,to:进入到哪个路由去,from:从哪个路由离开,next:函数,决定是否展示你要看到的路由页面。
import router from './router'
router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{
console.log(to,from)
next()
})
// 在导航被确认之前,同时在所有组件内守卫和异步路由组件被解析之后,解析守卫就被调用
router.beforeResolve((to,from,next)=>{
console.log(2)
next()
})
router.afterEach((to,from)=>{
console.log(to,from)
})
next 函数在任何给定的导航守卫中都被严格调用一次。它可以出现多于一次,但是只能在所有的逻辑路径都不重叠的情况下,否则钩子永远都不会被解析或报错。
// BAD
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (to.name !== 'Login' && !isAuthenticated) next({ name: 'Login' })
// 如果用户未能验证身份,则 `next` 会被调用两次
next()
})
// GOOD
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (to.name !== 'Login' && !isAuthenticated) next({ name: 'Login' })
else next()
})
# 独享守卫
用法与全局守卫一致。只是,将其写进其中一个路由对象中,只在这个路由下起作用。
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
},
{
path:'/give',
name:"Give",
beforeEnter : ( to , from , next ) => {
console.log("hello")
},
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/Give.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
# 组件内守卫beforeRouteEnter vm
beforeRouteEnter路由守卫还未获取到this对象,只能使用next回调中的vm来获取, beforeRouteEnter 是支持给 next 传递回调的唯一守卫。对于 beforeRouteUpdate 和 beforeRouteLeave 来说,this 已经可用了,所以不支持传递回调,因为没有必要了。
<template>
<div class="home">
<img alt="Vue logo" src="../assets/logo.png">
<HelloWorld msg="Welcome to Your Vue.js App"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// @ is an alias to /src
import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue'
export default {
name: 'Home',
components: {
HelloWorld
},
beforeRouteEnter:(to,from,next)=>{
next(vm=>{
// 通过“vm”访问组件实例`
//可以通过vm.name去访问data里面的name属性,跟this.name一样效果
console.log(this)
console.log("enter");
})
},
beforeRouteUpdate:(to,from,next)=>{
console.log(this)
console.log("update");
next()
},
beforeRouteLeave:(to,from,next)=>{
console.log(this)
console.log("leave")
next()
},
}
</script>
# 路由组件应用实例
beforeEnter+beforeEach登录跳转控制
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router'
const routes = [{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "home" */ '../views/home/Home')
},
{
path: '/login',
name: 'Login',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "login" */ '../views/login/Login'),
beforeEnter(to, from, next) {
const { isLogin } = localStorage;
isLogin ? next({ name: 'Home'}): next();
}
}
]
const router = createRouter({
history: createWebHashHistory(),
routes
})
router.beforeEach((to, from ,next) => {
const { isLogin } = localStorage;
const { name } = to;
const isLoginOrRegister = (name === "Login" || name === "Register");
(isLogin || isLoginOrRegister) ? next() : next({ name: 'Login'});
})
export default router
- fullpath重定向
router.beforeEach((to, from, next) => {
if (to.meta.auth) {
if (window.isLogin) {
next()
} else {
next('/login?redirect='+to.fullPath)
}
} else {
next()
}
})
{
path: '/about',
meta: {
auth: true
}
},
{
path: '/login',
component: () => import('../views/Login.vue')
},
// About.vue
beforeRouteEnter(to, from, next) {
if (window.isLogin) {
next();
} else {
next("/login?redirect=" + to.fullPath);
}
}
# 异步组件路由懒加载
集合webpack,异步组件不需要import引入在js中,好处是可以按需加载。除了首页,其他的可以触发加载。
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
# 动态添加路由表
当有可能涉及到权限页面时,就可以使用动态路由进行配置.使用方法为addRoutes.
<template>
<div id="app">
<div id="nav">
<div v-for="item in arr" >
<router-link :to="item.to">{{item.name}}</router-link> |
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import Vue from "vue"
export default{
name:"app",
data(){
return{
arr:[
{to:"/",name:"Home"},
{to:"/about",name:"About"},
]
}
},
mounted(){
const asyncRoute =
[{
path: '/wei',
name: 'Wei',
component: () => import('@/views/Wei'),
meta: {
title: '用户管理'
}
}]
console.log(asyncRoute)
this.$router.addRoutes([...asyncRoute])
let tem=[];
tem=asyncRoute.map(e=>{
return {to:e.path,name:e.name}
})
console.log(tem)
this.arr.push(...tem)
tem=null;
console.log(this.$router)
}
}
</script>
v4版本移除addRoutes方法,可以使用addRoute逐个添加
// 动态添加路由
const categoryRoute = {
path: "/category",
component: () => import("../pages/Category.vue")
}
// 添加顶级路由对象
router.addRoute(categoryRoute);
// 添加二级路由对象
router.addRoute("home", {
path: "moment",
component: () => import("../pages/HomeMoment.vue")
})
# 动态删除路由表

# vue-router push重复点击bug
this.$router.push("/about")两次触发同样的路由会报错
NavigationDuplicated: Avoided redundant navigation to current location: "/about".
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const originalPush = VueRouter.prototype.push
VueRouter.prototype.push = function push(location) {
return originalPush.call(this, location).catch(err => err)
}
# vue路由缓存 keep-alive
利用keepalive做组件缓存,保留组件状态,提高执行效率,同时为了避免缓存过多,还可以设置上限数量
<keep-alive include="about,home">
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
- 使用include或exclude时要给组件设置name
- 两个特别的生命周期:activated、deactivated
- 还可以动态化的控制include和exclude
//最多缓存max个数量,多了的话把前面缓存的替换掉
<keep-alive :include="['about']" max=10>
<router-view></router-view>
</keep-alive>
# 手写vue-router思路
- 使用vue-router插件,router.js
import Router from 'vue-router'
Vue.use(Router)
- 创建Router实例,router.js
export default new Router({...})
- 在根组件上添加该实例,main.js
import router from './router'
new Vue({
router,
}).$mount("#app");
- 添加路由视图,App.vue
<router-view></router-view>
- 实现一个插件
- 实现VueRouter类
- 处理路由选项
- 监控url变化,hashchange
- 响应这个变化
- 实现install方法
- $router注册
- 两个全局组件router-link router-view
- 实现VueRouter类
- 路由表展示
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from './myrouter.js'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
routes
})
export default router
- myrouter配置
let Vue;
class Myrouter{
constructor(arg) {
console.log('2',arg)
this.$$options =arg
Vue.util.defineReactive(this,'current',window.location.hash.slice(1)||"/")
window.addEventListener("hashchange", () => {
// #/about => /about
this.current = window.location.hash.slice(1);
// console.log(this.current)
});
}
push(v){
this.current = v || '/'
}
}
Myrouter.install = function (_vue){
Vue = _vue
console.log(1)
// console.log(Vue)
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
console.log(5)
if(this.$options.router){
Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router
}
}
})
Vue.component('router-link',{
props:{
to:{
type:String,
require:true
}
},
render(h){
console.log(3)
return h('a',{
attrs:{
href:"#"+this.to
}
},this.$slots.default)
}
})
Vue.component('router-view',{
render(h){
console.log(4)
let component1=null
const router =this.$router.$$options.routes.find((el)=> el.path === this.$router.current)
if(router){
component1 =router.component
}
return <component1/>
}
})
}
export default Myrouter
# 处理有children情况下的view-router
// 简单实现嵌套路由
// ① 记录当前路由router-view的深度
// ② 路由匹配,得到深度对应的组件
let Vue;
class Router {
constructor(options) {
this.$options = options;
this.routeMap = {};
// options.routes.forEach((route) => {
// this.routeMap[route.path] = route;
// });
// Vue.util.defineReactive(this, "current", window.location.hash.slice(1) || "/");
this.current = window.location.hash.slice(1) || "/";
window.addEventListener("hashchange", this.onHashchange.bind(this));
window.addEventListener("load", this.onHashchange.bind(this));
// 响应式数组
Vue.util.defineReactive(this, "matched", []);
this.match();
}
onHashchange() {
this.current = window.location.hash.slice(1);
// 页面刷新时,需要将matched数组置空,重新匹配路由
this.matched = [];
this.match();
}
// 通过 this.current 来匹配路由
match(routes) {
routes = routes || this.$options.routes;
for (const route of routes) {
if (route.path === "/" && this.current === "/") {
this.matched.push(route);
return;
}
// this.current : /about/info , route.path : /about 、 /about/info
if (route.path !== "/" && this.current.includes(route.path)) {
this.matched.push(route);
if (route.children) {
this.match(route.children);
}
console.log(this.matched)
return;
}
}
}
static install(_Vue) {
Vue = _Vue;
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate() {
if (this.$options.router) {
Vue.prototype.$router = this.$options.router;
}
},
});
Vue.component("router-link", {
props: {
to: {
type: String,
default: "",
},
},
render(h) {
return h("a", { attrs: { href: "#" + this.to } }, this.$slots.default);
},
});
Vue.component("router-view", {
render(h) {
// const { routeMap, current } = this.$router;
// console.log(current);
// const comp = (routeMap[current] && routeMap[current].component) || null;
// 计算出路由的深度
this.$vnode.data.routerView = true;
let depth = 0;
let parent = this.$parent;
while (parent) {
const vnodeData = parent.$vnode && parent.$vnode.data;
// parent的$vnode.data.routerView存在,即该parent组件也是一个router-view,那么组件的深度就要➕1
if (vnodeData && vnodeData.routerView) {
depth++;
}
parent = parent.$parent;
}
const route = this.$router.matched[depth]
const comp = route && route.component || null
return h(comp);
},
});
}
}
export default Router;
路由表中写render
{
path: '/about',
name: 'About',
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/About.vue'),
children:[{
path:"t1",
name:"T1",
component:{render(){return <div>children1</div>}}
}]
}
总结:手写vue路由,首先要有install方法,这个是写入组件的必备方法,同时需要添加route-link和router-view两个组件,在根组件声明时,利用mixin方法在beforecreate时混入$router到vue的原型对象上,同时监听路由的变化,由于路由可以是嵌套的,要做好层级关系,对应匹配,防止内存溢出。