# [vuex状态管理模式]
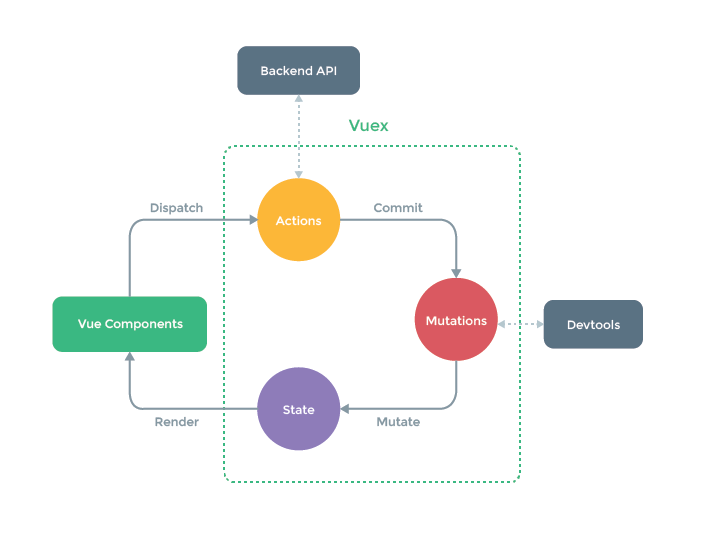
每一个Vuex应用的核心就是store(仓库)。“store”基本上就是一个容器,它包含着你的应用中大部分的状态 (state)。
# 安装vuex
npm install vuex --save
理解
vuex理解
是状态管理模式。它采用集中式存储管理应用的所有的状态,并以相应的规则保证状态以一种可预测的方式发生变化。可以理解为是一个全局变量
- state 数据中心
- mutations 操作数据
- actions 什么时候触发操作,执行动作,改变数据
# 使用vuex
# 创建一个store.js用来存取数据
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// state :localStorage.getItem('state') ? JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('state')) 刷新后保留数据的办法
state: {
count: 0,
todos: [
{ id: 1, text: '...', done: true },
{ id: 2, text: '...', done: false }
]
},
getters: {
// getter可以认为是store的计算属性
// getter正常接受两个参数,分别表示 state, getters(在使用module时,还会有根store的state和getters)
doubleCount: (state, getters) => {
return state.count * 2
},
doneTodos (state) {
return state.todos.filter(todo => todo.done)
},
//Getter 也可以接受其他 getter 作为第二个参数:
doneTodosCount (state, getters) {
return getters.doneTodos.length
}
},
mutations: {
increment (state) {
state.count++
},
addForNum (state, payload) {
state.count += Number(payload.num)
},
asyncAdd (state) {
state.count += 10
},
login(state){
}
},
actions: {
// 异步操作需要放在actions中执行,然后使用commit交给对应的mutations修改state的值
asyncAddAction (context) {
//这里的context和我们使用的$store拥有相同的对象和方法
setTimeout (function () {
context.commit('asyncAdd')
}, 500)
},
login({commit}, username) {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
if (username === 'admin') {
commit('login')
resolve()
} else {
reject()
}
}, 1000);
})
}
}
})
export default store
- Action 通常是异步的,那么如何知道 action 什么时候结束呢?可以通过让action返回Promise,在Promise的then中来处理完成后的操作;
- dispatch派发请求异步接受信息
this.$store.dispatch('login', 'admin').then(() => {
this.$router.push(this.$route.query.redirect)
}).catch(() => {
alert('用户名或密码错误')
})
# computed与vuex数据的结合运用
computed:{
category: {
get() {
return this.$store.state.category
},
set (value) {
console.log("Value of category changed")
this.store.commit("SET_CAT", value)
}
}
}
import { mapGetters } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapGetters(['name'])
}
# 在main.js里引用
import store from './store'
new Vue({
el: '#app',
router,
store,
components: { App },
template: '<App/>'
})
# 在vue文件中使用
<template>
<div>
<h2>这是计数器页面</h2>
<div>
<div>计数:{{count}}</div>
<div>双倍计数:{{doubleCount}}</div>
<br/>
<button @click="increment">+1</button>
<div>
增加值 <input type="text" v-model="num" />
<button @click="addForNum">=</button>
</div>
<div>
<button @click="asyncAdd">异步加10</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
name: 'index',
data () {
return {
num: 0
}
},
computed: {
count () {
return this.store.state.count
},
doubleCount () {
return this.store.getters.doubleCount
}
},
methods: {
// 自增1
increment () {
//this.$store.state.number++ //不推荐,严格模式无效
this.store.commit('increment')
},
// 加指定的值
addForNum () {
this.store.commit('addForNum', {num: this.num})
},
// 异步加1
asyncAdd () {
this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddAction')
}
}
}
</script>
# vuex的辅助函数
可以使用map辅助函数使代码更精简
- store文件中的内容不需要变动,只要在组件中使用map辅助函数来替代全局的this.$sotre下的属性和方法即可。
- 注意辅助函数mapGetters的对象写法,只有重命名,没有函数形式
<template>
<div>
<h2>这是计数器页面</h2>
<div>
<div>计数:{{count}} - {{countAlias}}</div>
<div>双倍计数:{{doubleCount}} - {{doubleCountAlias}}</div>
<br/>
<button @click="increment">+1</button>
<div>
增加值 <input type="text" v-model="num" />
<button @click="incrementBy(num)">=</button>
</div>
<div>
<button @click="asyncAdd">异步加10</button>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'index',
data () {
return {
num: 0,
localCount: 10
}
},
// computed:mapState(['a','b']),
//如果computed只获取store中的数据且不需要转换,那么可以直接使用mapState,不需要解构
//mapState本身返回的就是个对象
computed: {
/*
* ------------------------------------------------------------
* mapState
*/
// 【传统形式】
// count () {
// return this.store.state.count
// },
// 【对象形式】
...mapState({
// 箭头函数可使代码更简练
count: state => state.count,
// 传字符串参数 'count' 等同于 `state => state.count`
// 使用这种方式可以更简洁地为state生成的计算属性定义一个别名
countAlias: 'count',
// 为了能够使用 `this` 获取局部状态,必须使用常规函数
countPlusLocalState (state) {
return state.count + this.localCount
}
}),
// 【数组形式】
// 当映射的计算属性的名称与 state 的子节点名称相同时,我们也可以给 mapState 传一个字符串数组。
...mapState([
// 映射 this.count 为 store.state.count
'count'
]),
/*
* ------------------------------------------------------------
* mapGetters
*/
// 【传统形式】
// doubleCount () {
// return this.store.getters.doubleCount
// }
// 【对象形式】
// 如果你想将一个 getter 属性另取一个名字,使用对象形式
...mapGetters({
// 把 `this.doubleCountAlias` 映射为 `this.store.getters.doubleCount`
doubleCountAlias: 'doubleCount'
}),
// 【数组形式】
...mapGetters(['doubleCount'])
},
methods: {
/*
* ------------------------------------------------------------
* mapMutations
*/
// 【传统形式】
// 自增1
// increment () {
// this.store.commit('increment')
// },
// // 加指定的值
// incrementBy (amount) {
// this.store.commit('incrementBy', amount)
// },
// 【数组形式】
...mapMutations([
'increment', // 将 `this.increment()` 映射为 `this.store.commit('increment')`
// `mapMutations` 也支持载荷:
'incrementBy' // 将 `this.incrementBy(amount)` 映射为 `this.store.commit('incrementBy', amount)`
]),
// 【对象形式】
...mapMutations({
add: 'increment' // 将 `this.add()` 映射为 `this.store.commit('increment')`
}),
// // 异步加1
// asyncAdd () {
// this.store.dispatch('asyncAddAction')
// }
/*
* ------------------------------------------------------------
* mapActions
*/
// 【数组形式】
...mapActions([
'asyncAddAction', // 将 `this.asyncAddAction()` 映射为 `this.store.dispatch('asyncAddAction')`
]),
// 【对象形式】
...mapActions({
asyncAdd: 'asyncAddAction' // 将 `this.asyncAdd()` 映射为 `this.$store.dispatch('asyncAddAction')`
})
}
}
</script>
因为辅助函数返回的本来就是对象,所以要用一次展示运算符,除非是直接如computed:mapState(['xxx'])这种外层没加包裹形式
<button @click="login" v-if="!isLogin">登录</button>
当需要映射的值时模块化的值,如是user模块,可以用以下两种方式来写
import { mapState } from 'vuex'
computed: {
...mapState('user', ['isLogin']) //推荐,在template中可以直接使用isLogin
//...mapState(['user/isLogin']) // 不推荐,用的时候不好写
}
import { mapActions } from 'vuex'
methods: {
login() {
this['user/login']('admin').then(...)
},
...mapActions(['user/login', 'user/logout'])
//...mapActions(user,['login'])//这种写法也可以,但是如果methods中还有别的也叫login的方法就冲突了!!!
},
# vuex modules模块化设计
新建modules文件夹在store文件夹内,选项namesapced保证命名不冲突
+ store
+ modules
- a.js
- b.js
- index.js
//a.js b.js与之结构类似
const state={
count:1
}
const mutations={
add(state){
state.count++
}
}
const actions={
add:({commit})=>{
commit("add")
}
}
export default{
namespaced:true,
state,
mutations,
actions
}
//index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import count from './a'
import number from './b'
Vue.use(Vuex)
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules:{
count,
number
}
})
//项目main.js
import store from './store/modules/index.js'
<template>
<div class="home">
<div>{{$store.state.count.count}}</div>
<button @click="add">+</button>
<button @click="miss">-</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'Home',
data(){
return{
a:""
}
},
methods:{
add(){
this.$store.state.count.count++;
},
miss(){
this.$store.commit('count/add')//两种操作写法,效果一致
//对象写法风格
this.$store.commit({
type:'count/add'
})
}
}
}
</script>
提示
默认情况下,模块内部的action和mutation仍然是注册在全局的命名空间中的,也就是说,子模块中有mutation/action/getters中有某个属性或者方法funa,根模块也有,那么比如操作commit('funa'),都会触发!
- 默认情况下Getter 同样也默认注册在全局命名空间;(this.$store.state.a.b(正确)=>a模块下的state中的b,this.$store.getters.a.geta(错误),不需要.getters)
- 如果希望模块具有更高的封装度和复用性,可以添加 namespaced: true 的方式使其成为带命名空间的模块:
- 当模块被注册后,它的所有 getter、action 及 mutation 都会自动根据模块注册的路径调整命名;
$store.getters["home/doubleHomeCounter"]:home模块下的doubleHomeCounter
<template>
<div>
{{this.$store.state.count}}<br/>
{{count}}<br/>
{{this.$store.getters.changeCount}}<br/>
<el-button type="primary" @click="add">主要按钮</el-button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import {mapState} from 'vuex'
export default {
name: 'home',
computed: {
...mapState([
'count'
])
},
methods: {
add () {
this.$store.dispatch('addFun', 10) // actions this.$store.commit('add',10) //mutations
}
},
mounted: {
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {
count: 1
},
getters: {
changeCount: state => {
return state.count + 1
}
},
mutations: {
add (state, n) {
state.count = state.count + n
}
},
actions: {
addFun (context, n) {
context.commit('add', n)
}
}
})
export default store
总结
- modules模块使用需要在每个js里加上命名空间选项namespaced:true
- indexjs注意写法
- this.$store.commit('count/add')
# createNamespacedHelpers
可以使用 createNamespacedHelpers 创建基于某个命名空间辅助函数。它返回一个对象,对象里有新的绑定在给定命名空间值上的组件绑定辅助函数。
<template>
<div>
<hr>
<h2>{{ homeCounter }}</h2>
<h2>{{ doubleHomeCounter }}</h2>
<!-- <h2>{{ doubleRootCounter }}</h2> -->
<button @click="increment">home+1</button>
<button @click="incrementAction">home+1</button>
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { createNamespacedHelpers, mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } from "vuex";
import { useState, useGetters } from '../hooks/index'
const { mapState, mapGetters, mapMutations, mapActions } = createNamespacedHelpers("home")
export default {
computed: {
// 1.写法一:
// ...mapState({
// homeCounter: state => state.home.homeCounter
// }),
// ...mapGetters({
// doubleHomeCounter: "home/doubleHomeCounter"
// })
// 2.写法二:
...mapState("home", ["homeCounter"]),
...mapGetters("home", ["doubleHomeCounter"])
// 3.写法三:直接通过createNamespacedHelpers绑定对应的命名空间,可以不需要像写法二那样去处理
...mapState(["homeCounter"]),
...mapGetters(["doubleHomeCounter"])
},
methods: {
// 1.写法一:
// ...mapMutations({
// increment: "home/increment"
// }),
// ...mapActions({
// incrementAction: "home/incrementAction"
// }),
// 2.写法二
...mapMutations("home", ["increment"]),
...mapActions("home", ["incrementAction"]),
// 3.写法三:
...mapMutations(["increment"]),
...mapActions(["incrementAction"]),
},
setup() {
// {homeCounter: function}
const state = useState(["rootCounter"])
const rootGetters = useGetters(["doubleRootCounter"])
const getters = useGetters("home", ["doubleHomeCounter"])
const mutations = mapMutations(["increment"])
const actions = mapActions(["incrementAction"])
return {
...state,
...getters,
...rootGetters
...mutations,
...actions
}
}
}
</script>
- useState.js
import { mapState, createNamespacedHelpers } from 'vuex'
import { useMapper } from './useMapper'
export function useState(moduleName, mapper) {
let mapperFn = mapState
if (typeof moduleName === 'string' && moduleName.length > 0) {
mapperFn = createNamespacedHelpers(moduleName).mapState
} else {
mapper = moduleName
}
return useMapper(mapper, mapperFn)
}
- useMapper
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { useStore } from 'vuex'
export function useMapper(mapper, mapFn) {
// 拿到store独享
const store = useStore()
// 获取到对应的对象的functions: {name: function, age: function}
const storeStateFns = mapFn(mapper)
// 对数据进行转换
const storeState = {}
Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach(fnKey => {
const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({$store: store})
storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn)
})
return storeState
}
# require.context 借助webpack来读modules文件下文件,避免一个个手动引入
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import getters from './getters'
Vue.use(Vuex)
// https://webpack.js.org/guides/dependency-management/#requirecontext
const modulesFiles = require.context('./modules', true, /\.js$/)
// you do not need `import app from './modules/app'`
// it will auto require all vuex module from modules file
const modules = modulesFiles.keys().reduce((modules, modulePath) => {
// set './app.js' => 'app'
const moduleName = modulePath.replace(/^\.\/(.*)\.\w+$/, '$1')
const value = modulesFiles(modulePath)
modules[moduleName] = value.default
return modules
}, {})
console.log( modulesFiles,modules)
const store = new Vuex.Store({
modules,
getters
})
export default store
require.context(directory, useSubdirectories, regExp)
//directory: 要查找的文件路径
//useSubdirectories: 是否查找子目录
// regExp: 要匹配文件的正则
代码很简单,require.context执行后,返回一个方法webpackContext,这个方法又返回一个__webpack_require__,
这个__webpack_require__就相当于require或者import。同时webpackContext还有二个静态方法keys与resolve,一个id属性。
keys: 返回匹配成功模块的名字组成的数组
resolve: 接受一个参数request,request为test文件夹下面匹配文件的相对路径,返回这个匹配文件相对于整个工程的相对路径
id: 执行环境的id,返回的是一个字符串,主要用在module.hot.accept,应该是热加载
# vuex严格模式
无论何时发生了状态变更且不是由 mutation 函数引起的,将会抛出错误。这能保证所有的状态变更都能被调试工具跟踪到。开启严格模式 strict: true
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
strict: true
})
# vuex插件写法
Vuex 的 store 接受 plugins 选项,这个选项暴露出每次 mutation 的钩子。Vuex 插件就是一个函数,它接收 store 作为唯一参数:
const myPlugin = store => {
// 当 store 初始化后调用
}
注册插件:
import myPlugin from "xxx"
const store = new Vuex.Store({
// ...
plugins: [myPlugin]
})
范例:实现登录状态持久化,store/plugins/persist.js
- store.subscribe插件中的方法,可以监听到对应的mutation state变更信息,同步操作
export default store => {
// 初始化时从localStorage获取数据
if(localStorage) {
const user = JSON.parse(localStorage.getItem('user'))
if (user) {
store.commit('user/login')
store.commit('user/setUsername', user.username)
}
}
// 用户状态发生变化时缓存之
store.subscribe((mutation, state) => {
if (mutation.type.startsWith('user/')) {
localStorage.setItem('user', JSON.stringify(state.user))
} else if (mutation.type === 'user/logout') {
localStorage.removeItem('user')
}
})
}
- 借助vuex-createPersistedState插件实现缓存数据。
import createPersistedState from 'vuex-createPersistedState'
const PERSIST_PATHS = ['user']
const store = new Vuex.Store({
state: {},
modules: {
app,
settings,
user,
permission,
tagsView
},
getters,
plugins: [createPersistedState({
storage: window.sessionStorage,
paths: PERSIST_PATHS
})]
})
# vuex手写
- 实现插件
-实现Store类
- 维持1个响应式状态state
- 实现commit()
- 实现dispatch()
- getters
- 挂载$store
let Vue
class Store{
constructor(option = {}) {
this.$option = option
console.log(option)
this._wrapgetters =option.getters
const computed ={}
this.getters ={}
const store =this
Object.keys(this._wrapgetters).forEach(key=>{
//获取用户定义的getters
console.log(store,store._wrapgetters)
const fn = store._wrapgetters[key]
//转化为computed可以使用无参形式
computed[key] =function(){
return fn(store.state)
}
Object.defineProperty(store.getters,key,{
get:()=>store.vm[key]
})
})
console.log(computed)
this.vm = new Vue({
data:{
state:option.state
},
computed
})
this.mutations =option.mutations
this.actions =option.actions
this.commit =this.commit.bind(this)
this.dispatch =this.dispatch.bind(this)
}
get state(){
return this.vm.state
}
set state(v){
console.error("warning",'do not to change state')
}
commit(v,t){
console.log(this)
// 需要在constructor中给commit方法绑定好this的指向,否则调用会undefined
// console.log(this.mutations[v])
// console.log(this.vm.state,t)
if(v){
this.mutations[v](this.vm.state,t)
}
}
dispatch(v){
// console.log(v)
console.log(this.actions[v])
console.log(this)
if(v){
this.actions[v](this,v)
}
}
}
function install(vue){
Vue = vue
Vue.mixin({
beforeCreate(){
// console.log('beforeCreate')
if(this.$options.store){
Vue.prototype.$store = this.$options.store
}
}
})
}
export default {Store,install}
# vue3中使用vuex
- vuex创建的写法上与之前的也有所不同
- getters类似computed,他返回的是该函数的计算结果,当然也可以返回函数,那么就可以再传递一个可用参数实现复用
import { createStore } from "vuex"
import home from './modules/home'
import user from './modules/user'
const store = createStore({
state() {
return {
rootCounter: 100
}
},
getters: {
doubleRootCounter(state) {
return state.rootCounter * 2
},
totalPriceCountGreaterN(state, getters) {
return function(n) {
let totalPrice = 0
for (const book of state.books) {
if (book.count > n) {
totalPrice += book.count * book.price
}
}
return totalPrice * getters.currentDiscount
}
}
},
mutations: {
increment(state) {
state.rootCounter++
}
},
modules: {
home,
user
}
});
export default store;
# 在setup辅助函数的使用
在setup中,computed里面只能放函数形式,不能类似options中的可以以对象的形式放多个computed的属性,要么一个state使用一个computed,要么通过遍历的方式,利用hooks去处理。mapState返回的其实每个属性就是函数。同样可以对mapGetters进行相同的封装。
import { computed } from 'vue'
import { mapState, useStore } from 'vuex'
export function useState(mapper) {
// 拿到store独享
const store = useStore()
// 获取到对应的对象的functions: {name: function, age: function}
const storeStateFns = mapState(mapper)
// 对数据进行转换
const storeState = {}
Object.keys(storeStateFns).forEach(fnKey => {
const fn = storeStateFns[fnKey].bind({$store: store})
storeState[fnKey] = computed(fn)
})
return storeState
}
<template>
<div>
<h2>Home:{{ $store.state.counter }}</h2>
<hr>
<h2>{{counter}}</h2>
<h2>{{name}}</h2>
<h2>{{sCounter}}</h2>
<h2>{{sName}}</h2>
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<script>
// import { computed } from 'vue'
import { useState } from '../hooks/useState'
export default {
setup() {
// const sCounter = computed(() => store.state.counter)//默认写法
const storeState = useState(["counter", "name"])
const storeState2 = useState({
sCounter: state => state.counter,
sName: state => state.name
})
return {
...storeState,
...storeState2
}
}
}
</script>
# mutation在setup中使用
在setup中使用mutation比较简单,不需要像state和getters那样麻烦
<template>
<div>
<h2>当前计数: {{ $store.state.counter }}</h2>
<hr>
<button @click="increment">+1</button>
<button @click="add">+1</button>
<button @click="decrement">-1</button>
<button @click="increment_n({n: 10})">+10</button>
<hr>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'
import { INCREMENT_N } from '../store/mutation-types'
export default {
methods: {
...mapMutations(["increment", "decrement", INCREMENT_N]),
...mapMutations({
add: "increment"
})
},
setup() {
const storeMutations = mapMutations(["increment", "decrement", INCREMENT_N])
return {
...storeMutations
}
}
}
</script>
<style scoped>
</style>