# redux进阶
# UI组件 和 容器组件
ui组件主要是render函数那部分内容,渲染页面样式的组件,而容器组件则是逻辑部分。
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import {Input,Button,List} from 'antd'
class AppUI extends Component {
render(){
return (
<div style={{marginTop:'10px',marginLeft:'10px'}}>
<Input style={{width:'300px'}}
placeholder="请输入内容"
onChange={this.props.inputchange}
value={this.props.inputValue}
/>
<Button
type="primary"
style={{marginLeft:'10px'}}
onClick={this.props.btn}
>提交</Button>
<List
size="small"
style={{width:'300px',marginTop:'10px'}}
bordered
dataSource={this.props.list}
renderItem={(item,i) => (
<List.Item style={{cursor:'pointer'}} onClick={(i)=>{
this.props.del(i)
}}>{item}</List.Item>
)}
/>
</div>
);
}
}
export default AppUI;
//父组件,包括state和一些操作方法,都可以传给子组件
render() {
return (
<AppUI
inputchange={this.inputchange}
inputValue={this.state.inputValue}
btn={this.btn}
list={this.state.list}
del={this.del}
/>
);
}
# 无状态组件
当一个普通组件只有render函数时,完全可以改写成一个无状态组件的形式
- 无状态组件的性能比较高
接受参数props
const AppUI=(props)=>{
return (
<div style={{marginTop:'10px',marginLeft:'10px'}}>
。。。
</div>
);
}
export default AppUI;
# redux中间件
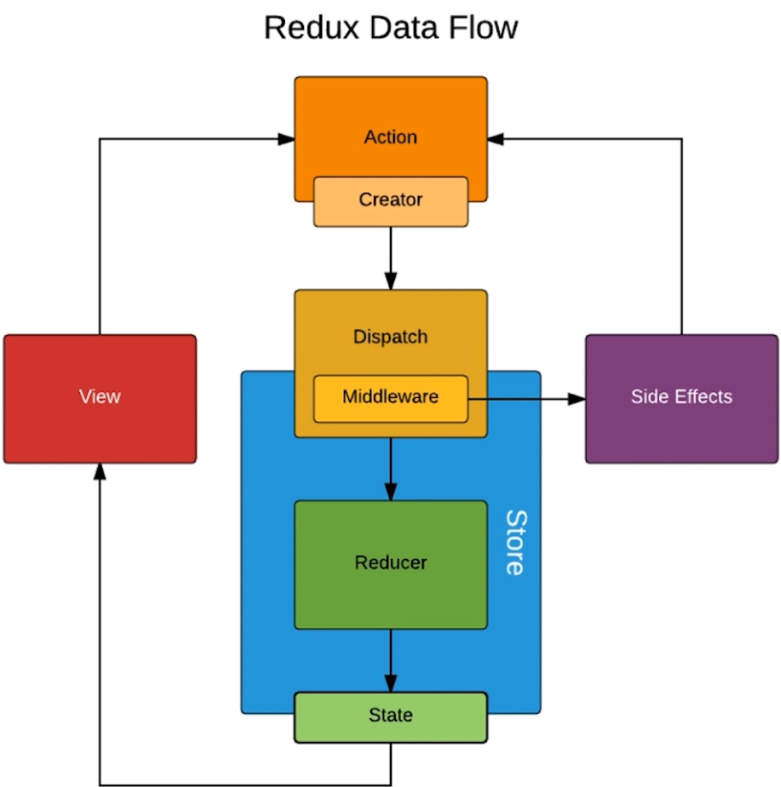
# redux-thunk
cnpm install redux-thunk --save
可以在actionCreators里通过返回一个函数,然后就可以在函数里编写某些异步操作了,待异步操作结束,最后通过传入的store.dispatch,发出action通知给Store要进行状态更新。
//store/index.js
import {createStore,compose,applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer.js'
import thunk from 'redux-thunk'
const composeEnhancers =window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ ?
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({}) : compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(
applyMiddleware(thunk),
);
//如果不需要使用多个中间件,如不使用window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__,
//createStore第二个参数可以直接写成applyMiddleware(thunk)
const store =createStore(
reducer,
enhancer
);
export default store;
- 返回给store的每个action一般只能写成对象的形式,但是通过使用react-thunk之后,action可以返回函数,
而且不需要引入store因为他自带dispatch这个方法
//actionCreators.js
export const getInputValue=(value)=>({
type:'change_input_value',
value
})
export const orgin=(value)=>({
type:"orgin",
value
})
// 如果没有配置react-thunk,那么在actionCreator中使用返回的是函数会报错
// Actions must be plain objects. Use custom middleware for async actions.
// 还可以进行异步操作,比如像后台发起请求等候反馈结果
export const getorgin= ()=>{
return (dispatch) => {
setTimeout(()=>{
const res=[1,2,3,4,5,6];
const action=orgin(res)
dispatch(action)
},3000)
}
}
//App.js
componentDidMount(){
const action =getorgin();
store.dispatch(action)
}
# redux-saga
redux-saga 是一个用于管理 Redux 应用异步操作的中间件(又称异步 action)。 redux-saga 通过创建 Sagas 将所有的异步操作逻辑收集在一个地方集中处理。
- Reducers 负责处理 action 的 state 更新
- Sagas 负责协调那些复杂或异步的操作
没使用redux-saga,action接收只能在reducer,而现在可以在sagas.js中也可以接收到。
redux增加中间件处理副作用后的数据流大致如下:UI——>action(side function)—>middleware—>action(plain)—>reducer—>state—>UI
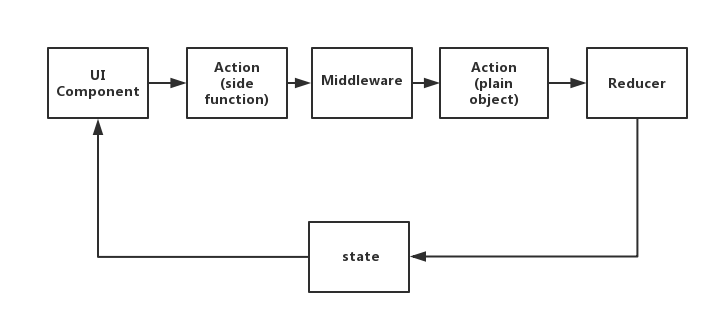
在有副作用的action和原始的action之间增加中间件处理,从图中我们也可以看出,中间件的作用就是:转换异步操作,生成原始的action,这样,reducer函数就能处理相应的action,从而改变state,更新UI。
# redux-saga的关键字
# fork:创建一个新的进程或者线程,并发发送请求。
function* user() {
yield takeEvery('FETCH_REQUEST', fetch_user); // 监听 FETCH_REQUEST action
}
// 并发发送请求
function* fetch_user() {
const [users, todos] = [
yield fork(fetchResource, 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users'),
yield fork(fetchResource, 'https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos')
]
}
function* fetchResource(resource) {
const data = yield call(axios.get, resource);
// 获取 call 数据,触发成功后的 action
yield put({ type: 'FETCH_SUCESS', uu: data });
}
# call:发送 api 请求
# put:发送对应的 dispatch,触发对应的 action
# takeEvery:监听对应的 action;每一次 dispatch 都会触发;例如:点击一个新增的按钮,2s 后触发新增动作,在2s内不断点击按钮,这时候,每一次点击,都是有效的。
# takeLatest:监听对应的 action;只会触发最后一次 dispatch;例如:点击一个新增的按钮,2s 后触发新增动作,在2s内不断点击按钮,这时候,只有最后一次点击是有效的。
# all:跟 fork 一样,同时并发多个 action,没有顺序。
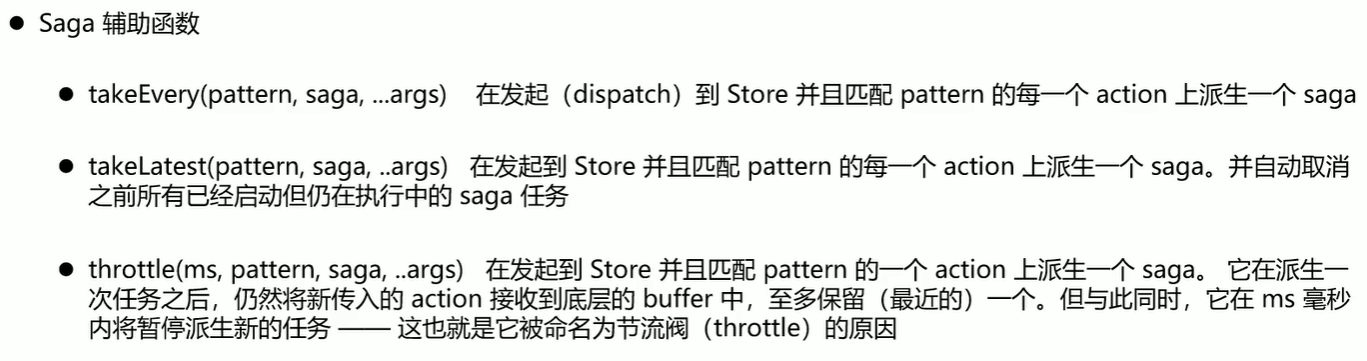
const rootUser = [
user(),
todo()
];
yield all([ // 同时并发多个
...rootUser, //
add()
]);
cnpm install redux-saga --save
- createSagaMiddleware(options) 创建一个 Reudx middlerware,并将sagas链接到Redux Store,通过第三个参数传入。
- middleware.run(saga,...args) 动态运行saga,只能用于在applyMiddleware运行
- saga:一个generator函数
- arg:提供saga的参数
import {createStore,compose,applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer.js'
import mySaga from "./sagas.js"
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware()
createStore(reducer,{},applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware))
sagaMiddleware.run(mySaga)
//store/index.js
import {createStore,compose,applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import reducer from './reducer.js'
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'
import mySaga from "./sagas.js"
const sagaMiddleware=createSagaMiddleware();
const composeEnhancers =window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__ ?
window.__REDUX_DEVTOOLS_EXTENSION_COMPOSE__({}) : compose;
const enhancer = composeEnhancers(
applyMiddleware(sagaMiddleware),
);
const store =createStore(
reducer,
enhancer
);
sagaMiddleware.run(mySaga)
export default store;
//App.js
componentDidMount(){
const action ={
type:"getorgin"
};
console.log(action)
store.dispatch(action)
}
import {takeEvery,put} from 'redux-saga/effects'
function* doit(v){
let res=[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8];
const action={
type:'orgin',
value:res
}
yield put(action)
}
function* mySaga(){
yield takeEvery('getorgin',doit)
}
export default mySaga
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import {createStore, applyMiddleware} from 'redux'
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga'
import rootSaga from './sagas'
import Counter from './Counter'
import rootReducer from './reducers'
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware()
let middlewares = []
middlewares.push(sagaMiddleware)
const createStoreWithMiddleware = applyMiddleware(...middlewares)(createStore)
const store = createStoreWithMiddleware(rootReducer)
sagaMiddleware.run(rootSaga)
const action = type => store.dispatch({ type })
function render() {
ReactDOM.render(
<div>
<h1>redux-saga</h1>
<Counter
value={store.getState()}
onIncrement={() => action('INCREMENT')}
onDecrement={() => action('DECREMENT')}
onIncrementAsync={() => action('INCREMENT_ASYNC')} />
</div>
,
document.getElementById('root')
)
}
render()
store.subscribe(render)
/**
* Created by guangqiang on 2017/12/17.
*/
import { put, call, take,fork ,takeEvery, takeLatest } from 'redux-saga/effects';
// import {} from 'redux-saga'
export const delay = ms => new Promise(resolve => setTimeout(resolve, ms));
function* incrementAsync() {
// 延迟 1s 在执行 + 1操作
yield call(delay, 1000);
yield put({ type: 'INCREMENT' });
}
export default function* rootSaga() {
// 如果没有while循环,只会执行一次;那样上面的onIncrementAsync只会执行一次
// while(true){
// yield take('INCREMENT_ASYNC');
// yield fork(incrementAsync);
// }
// 下面的写法与上面的写法上等效
yield takeEvery("INCREMENT_ASYNC", incrementAsync)
}
总结
- redux-thunk
- 需要在indexjs中引入redux的compose,applyMiddleware这两个组件
- 它的作用是让actionCreators能返回一个函数
- redux-saga
- 需要更多的配置,同时新建一个sagas.js文件来处理接受到的action
- 使用generator函数,注意语法
- 如果sagas.js和reducer中都对同一个action.type进行了处理,如果结果中有些改了同一个值的话,可能sagas.js最后会覆盖掉reducer的操作, 所以必须尽量避免这种情况
# react-redux
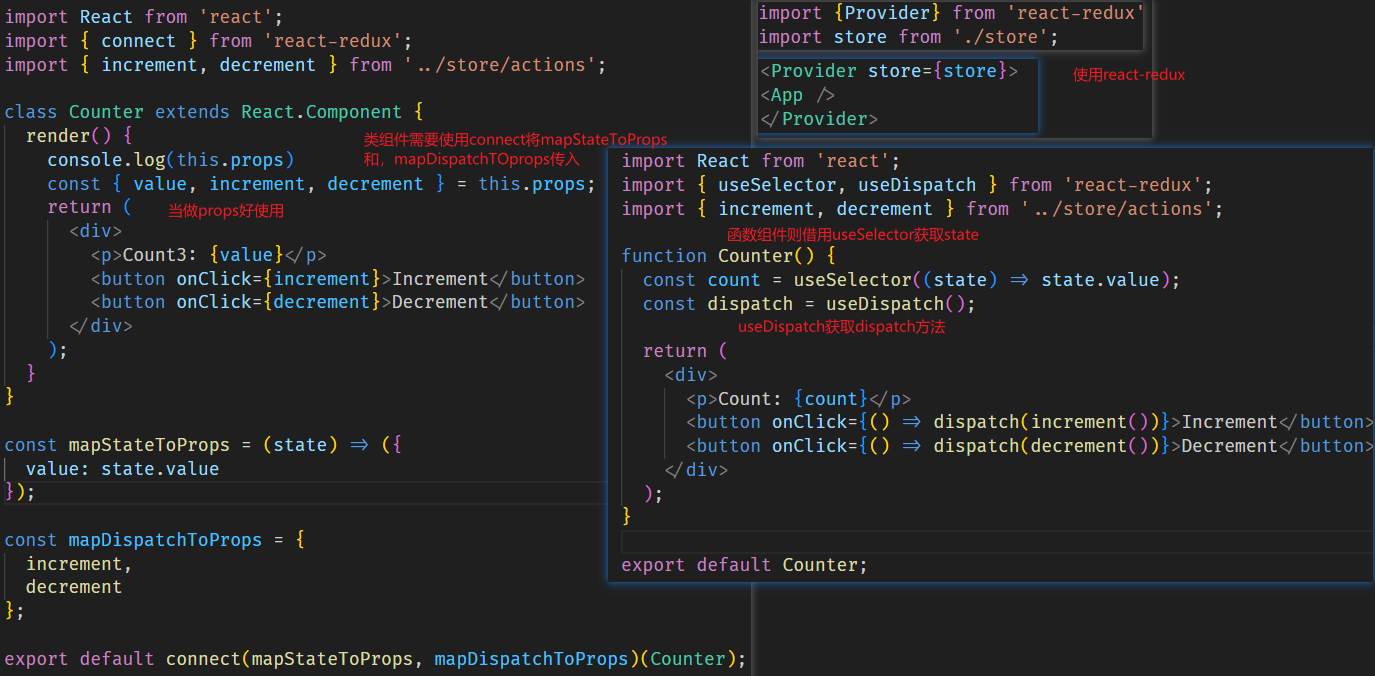
相对于只使用redux,要频繁手动订阅取消订阅,派发dispatch等操作,react-redux就轻松多了
cnpm install react-redux --save
react-redux提供了两个api
- Provider 为后代组件提供store
- connect 为组件提供数据和变更方法
- useSelector 和 useDispatch 钩子,供函数组件使用
provider绑定了store后,它包裹的组件都可以访问store里的信息,
import {Provider} from 'react-redux';
import store from './store';
const Apps=(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>
)
ReactDOM.render(Apps , document.getElementById('root'));
- 在使用的界面中配置,使用connect进行连接 ,注意结尾的写法使用connect
- 默认的dispatch方法其实是不需要通过mapDispatchToProps(名字随便取)导出的,但是利用mapDispatchToProps可以自定义dispatch名称,可以使对象形式,也可以是函数形式,函数形式默认接受一个参数dispatch
- 在组件中用这些需要解构props,来获取这些数据
import React,{Component} from 'react'
import {connect} from 'react-redux'
class Reactredux extends Component{
render() {
const { num,list, add, minus } = this.props;
return (
<div>
<h1>ReactReduxPage</h1>
<p>{num}</p>
<p>{list}</p>
<button onClick={add}>add</button>
<button onClick={minus}>minus</button>
</div>
);
}
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
console.log(state)
return {
num:state.counter,
list:state.china
};
};
// const mapDispatchToProps =(dispatch)=> {
// return{
// minus(){
// const action = {
// type:'INCREMENT'
// }
// dispatch(action)
// }
// }
// };
const mapDispatchToProps = {
add: () => {
return { type: "ADD_TODO" ,text:'19999'};
}
};
export default connect(
mapStateToProps, //状态映射 mapStateToProps
mapDispatchToProps, //派发事件映射
)(Reactredux);
redux-thunk解读 (opens new window) redux-saga文档 (opens new window) redux-saga解读 (opens new window) redux-saga合并 (opens new window)
# Redux Toolkit @reduxjs/toolkit
Redux Toolkit是Redux官方推荐的构建Redux逻辑的方式,它提供了更加简化、更加一致的API来管理Redux应用的状态。
通常结合react-redux用
npm install @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux
# 或者
yarn add @reduxjs/toolkit react-redux
1.在项目的根目录或 store 文件夹下创建一个 index.ts 或 index.js 文件,用于配置和导出 Redux store。
// store/index.js
import { configureStore } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
import userSlice from './slice/userSlice'; // 假设你有一个 userSlice 文件
import mySlice from './slice/mySlice'; // 假设你有一个 mySlice 文件
const store = configureStore({
reducer: {
user: userSlice.reducer, // 注意这里的命名空间 user
my: mySlice.reducer, // 注意这里的命名空间 my
},
// 你可以在这里添加额外的中间件配置,但 @reduxjs/toolkit 默认已经包含了 Redux Thunk
});
export default store;
- 创建 Slice. Slice 是 Redux Toolkit 引入的一个新概念,它将 action creators 和 reducer 逻辑组合在一起,使得每个模块化的 Redux 逻辑都封装在一个 slice 文件中。
// store/slice/userSlice.js
import { createSlice, createAsyncThunk } from '@reduxjs/toolkit';
// 定义一个异步函数,例如从服务器获取用户数据
export const fetchUserData = createAsyncThunk(
'user/fetchUserData',
async (userId, thunkAPI) => {
const response = await fetch(`https://api.example.com/users/${userId}`);
return response.json();
}
);
const userSlice = createSlice({
name: 'user', // slice 的命名空间
initialState: {
users: [], // 初始状态
loading: false,
error: null,
},
reducers: {
setUser: (state, action) => {
state.users = action.payload;
},
},
extraReducers: (builder) => {
builder
.addCase(fetchUserData.pending, (state) => {
state.loading = true;
state.error = null;
})
.addCase(fetchUserData.fulfilled, (state, action) => {
state.loading = false;
state.users = action.payload;
})
.addCase(fetchUserData.rejected, (state, action) => {
state.loading = false;
state.error = action.error.message;
});
},
});
export const { setUser } = userSlice.actions;
export default userSlice.reducer;
- 在组件中使用:在你的 React 组件中,可以使用 useSelector 和 useDispatch 钩子来访问 Redux store 中的状态和派发 actions。
// MyComponent.js
import React from 'react';
import { useSelector, useDispatch } from 'react-redux';
import { fetchUserData, setUser } from '../store/slice/userSlice';
const MyComponent = () => {
const users = useSelector((state) => state.user.users);
const loading = useSelector((state) => state.user.loading);
const dispatch = useDispatch();
React.useEffect(() => {
dispatch(fetchUserData(1)); // 假设我们要获取 ID 为 1 的用户数据
}, [dispatch]);
return (
<div>
{loading ? (
<p>Loading...</p>
) : (
<ul>
{users.map((user) => (
<li key={user.id}>{user.name}</li>
))}
</ul>
)}
</div>
);
};
export default MyComponent;
- 在应用入口文件中提供 Store
// index.js
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import store from './store'; // 导入创建的 Redux store
import App from './App'; // 导入的根组件
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
);