# vue3+ts项目
# EditorConfig编辑配置
让不同电脑系统不同编译器保证代码风格一致。 官网 (opens new window)
配置.editorconfig文件,编辑器会自动读取,不过vscode需要安装插件:EditorConfig for VS Code
root = true
[*] # 表示所有文件适用
charset = utf-8 # 设置文件字符集为 utf-8
indent_style = space # 缩进风格(tab | space)
indent_size = 2 # 缩进大小
end_of_line = lf # 控制换行类型(lf | cr | crlf)
trim_trailing_whitespace = true # 去除行首的任意空白字符
insert_final_newline = true # 始终在文件末尾插入一个新行
[*.md] # 表示仅 md 文件适用以下规则
max_line_length = off
trim_trailing_whitespace = false
# 使用prettier工具
vscode 安装插件 Prettier - Code formatter
Prettier 是一款强大的代码格式化工具,支持 JavaScript、CSS、Vue、GraphQL、JSON、Markdown 等语言,基本上前端能用到的文件格式它都可以搞定。
- 安装prettier
npm install prettier -D
- 配置.prettierrc文件:
- useTabs:使用tab缩进还是空格缩进,选择false;
- tabWidth:tab是空格的情况下,是几个空格,选择2个;
- printWidth:当行字符的长度,推荐80,也有人喜欢100或者120;
- singleQuote:使用单引号还是双引号,选择true,使用单引号;
- trailingComma:在多行输入的尾逗号是否添加,设置为
none; - semi:语句末尾是否要加分号,默认值true,选择false表示不加;
{
"useTabs": false,
"tabWidth": 2,
"printWidth": 80,
"singleQuote": true,
"trailingComma": "none",
"semi": false
}
- 创建.prettierignore忽略文件
/dist/*
.local
.output.js
/node_modules/**
**/*.svg
**/*.sh
/public/*
- 测试prettier是否生效
- 测试一:在代码中保存代码;
- 测试二:配置一次性修改的命令;
在package.json中配置一个scripts:
"prettier": "prettier --write ."
# 使用ESLint检测
- VSCode需要安装ESLint插件:
- 解决eslint和prettier冲突的问题:
安装插件:(vue在创建项目时,如果选择prettier,那么这两个插件会自动安装)
npm i eslint-plugin-prettier eslint-config-prettier -D
添加prettier插件:
extends: [
"plugin:vue/vue3-essential",
"eslint:recommended",
"@vue/typescript/recommended",
"@vue/prettier",
"@vue/prettier/@typescript-eslint",
'plugin:prettier/recommended'
],
# git Husky和eslint
虽然已经要求项目使用eslint了,但是不能保证组员提交代码之前都将eslint中的问题解决掉了:
也就是我们希望保证代码仓库中的代码都是符合eslint规范的;
那么我们需要在组员执行
git commit命令的时候对其进行校验,如果不符合eslint规范,那么自动通过规范进行修复;
那么如何做到这一点呢?可以通过Husky工具:
- husky是一个git hook工具,可以帮助我们触发git提交的各个阶段:pre-commit、commit-msg、pre-push
如何使用husky呢?
这里可以使用自动配置命令:
npx husky-init
npm install
这里会做三件事:
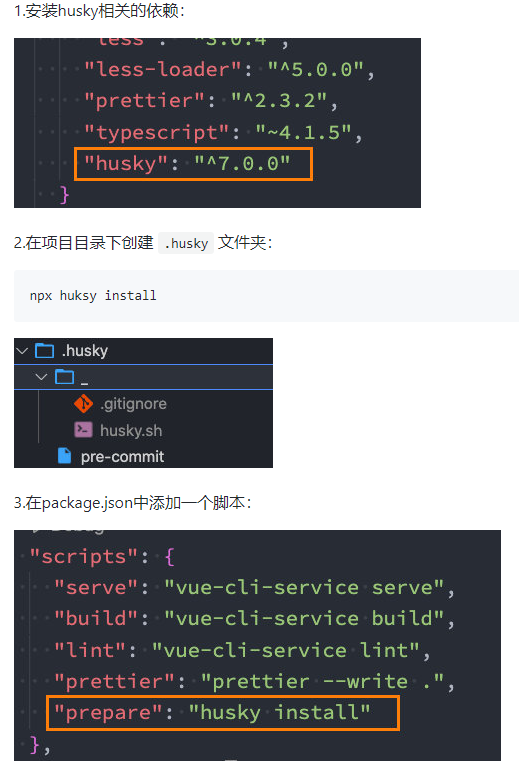
接下来,需要去完成一个操作:在进行commit时,执行lint脚本:
"scripts": {
"lint": "vue-cli-service lint --fix",
"prepare": "husky install"
},
.husky>pre-commit
#!/usr/bin/env sh
. "$(dirname -- "$0")/_/husky.sh"
npm run lint
# git commit规范 Commitizen
- Commitizen
cnpm install commitizen -D
- 安装cz-conventional-changelog,并且初始化cz-conventional-changelog:
npx commitizen init cz-conventional-changelog --save-dev --save-exact
这个命令会帮助安装cz-conventional-changelog:
并且在package.json中进行配置:
{
"scripts": {
"serve": "vue-cli-service serve",
"build": "vue-cli-service build",
"lint": "vue-cli-service lint --fix",
"prettier": "prettier --write . ",
"prepare": "husky install"
},
"dependencies": {
"core-js": "^3.6.5",
"vue": "^3.0.0"
},
"devDependencies": {
"commitizen": "^4.2.5",
"cz-conventional-changelog": "^3.3.0",
},
"config": {
"commitizen": {
"path": "./node_modules/cz-conventional-changelog"
}
}
}
这个时候提交代码需要使用 npx cz:
| Type | 作用 |
|---|---|
| feat | 新增特性 (feature) |
| fix | 修复 Bug(bug fix) |
| docs | 修改文档 (documentation) |
| style | 代码格式修改(white-space, formatting, missing semi colons, etc) |
| refactor | 代码重构(refactor) |
| perf | 改善性能(A code change that improves performance) |
| test | 测试(when adding missing tests) |
| build | 变更项目构建或外部依赖(例如 scopes: webpack、gulp、npm 等) |
| ci | 更改持续集成软件的配置文件和 package 中的 scripts 命令,例如 scopes: Travis, Circle 等 |
| chore | 变更构建流程或辅助工具(比如更改测试环境) |
| revert | 代码回退 |
# 代码提交验证
如果按照cz来规范了提交风格,但是依然有同事通过 git commit 按照不规范的格式提交应该怎么办呢?
可以通过commitlint来限制提交;
- 安装 @commitlint/config-conventional 和 @commitlint/cli
cnpm i @commitlint/config-conventional @commitlint/cli -D
- 在根目录创建commitlint.config.js文件,配置commitlint
module.exports = {
extends: ['@commitlint/config-conventional']
}
- 使用husky生成commit-msg文件,验证提交信息:
npx husky add .husky/commit-msg "npx --no-install commitlint --edit $1"
因为这条语句里包含着$1,它是在shell命令中代表的是参数。而Windows系统的cmd是没有$1这种操作符。
首先要搞明白这条命令做了什么事情:
- 添加一个文件commit-msg
- 然后再commit-msg中填充该npx指令
解决:直接把步骤分开执行就可以解决
- 添加一个文件commit-msg在.husky文件夹下, 执行下面命令
npx husky add .husky/commit-msg
- 在创建后的文件夹commit-msg文件里直接填充你的指令即可:npx --no-install commitlint
# 项目中eslint.js其他配置
module.exports = {
root: true,
env: {
node: true
},
extends: [
'plugin:vue/vue3-essential',
'eslint:recommended',
'@vue/typescript/recommended',
'@vue/prettier',
'@vue/prettier/@typescript-eslint',
'plugin:prettier/recommended'
],
parserOptions: {
ecmaVersion: 2020
},
rules: {
'no-console': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'warn' : 'off',
'no-debugger': process.env.NODE_ENV === 'production' ? 'warn' : 'off',
'@typescript-eslint/no-var-requires': 'off',//项目中有使用require,eslint想要统一成import,会报红色警告,可以配置关闭
'@typescript-eslint/no-explicit-any': 'off'
}
}
# ts中创建路由
import { createRouter, createWebHashHistory } from 'vue-router'
import type { RouteRecordRaw } from 'vue-router'// 这是vue-router内部定义好的
// 加上type表示这是类型而不是函数等,type可以省略
const routes: RouteRecordRaw[] = [
{
path: '/',
redirect: '/login'
},
{
path: '/login',
component: () => import('@/views/login/login.vue')
},
{
path: '/main',
component: () => import('@/views/main/main.vue')
}
]
const router = createRouter({
routes,
history: createWebHashHistory()
})
export default router
# shims-vue.d.ts
配置了某些插件,在template中直接使用$store会报红,需要在这里声明配置一下
/* eslint-disable */
declare module '*.vue' {
import type { DefineComponent } from 'vue'
const component: DefineComponent<{}, {}, any>
export default component
}
declare let $store: any
# ts封装axios
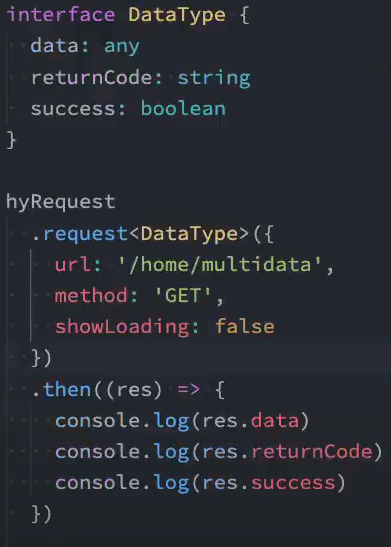
实现目标:
- 返回值约束,比如res.date时报错,避免代码写错
- 传入约束
// 请求出口
import HYRequest from './request'
// 基本配置根据不同的环境返回不同的url timeout
import { BASE_URL, TIME_OUT } from './request/config'
const hyRequest = new HYRequest({
baseURL: BASE_URL,
timeout: TIME_OUT,
interceptors: {
requestInterceptor: (config) => {
// 携带token的拦截
const token = ''
if (token) {
config.headers.Authorization = `Bearer ${token}`
}
console.log('请求成功的拦截')
return config
},
requestInterceptorCatch: (err) => {
console.log('请求失败的拦截')
return err
},
responseInterceptor: (res) => {
console.log('响应成功的拦截')
return res
},
responseInterceptorCatch: (err) => {
console.log('响应失败的拦截')
return err
}
}
})
export default hyRequest
- request/index.ts
import axios from 'axios'
import type { AxiosInstance } from 'axios'
//type
import type { HYRequestInterceptors, HYRequestConfig } from './type'
import { ElLoading } from 'element-plus'
import { ILoadingInstance } from 'element-plus/lib/el-loading/src/loading.type'
const DEAFULT_LOADING = true
class HYRequest {
instance: AxiosInstance
interceptors?: HYRequestInterceptors
showLoading: boolean
loading?: ILoadingInstance
constructor(config: HYRequestConfig) {
// 创建axios实例
this.instance = axios.create(config)
// 保存基本信息
this.showLoading = config.showLoading ?? DEAFULT_LOADING
this.interceptors = config.interceptors
// 使用拦截器
// 1.从config中取出的拦截器是对应的实例的拦截器
this.instance.interceptors.request.use(
this.interceptors?.requestInterceptor,
this.interceptors?.requestInterceptorCatch
)
this.instance.interceptors.response.use(
this.interceptors?.responseInterceptor,
this.interceptors?.responseInterceptorCatch
)
// 2.添加所有的实例都有的拦截器
this.instance.interceptors.request.use(
(config) => {
console.log('所有的实例都有的拦截器: 请求成功拦截')
if (this.showLoading) {
this.loading = ElLoading.service({
lock: true,
text: '正在请求数据....',
background: 'rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.5)'
})
}
return config
},
(err) => {
console.log('所有的实例都有的拦截器: 请求失败拦截')
return err
}
)
this.instance.interceptors.response.use(
(res) => {
console.log('所有的实例都有的拦截器: 响应成功拦截')
// 将loading移除
this.loading?.close()
const data = res.data
if (data.returnCode === '-1001') {
console.log('请求失败~, 错误信息')
} else {
return data
}
},
(err) => {
console.log('所有的实例都有的拦截器: 响应失败拦截')
// 将loading移除
this.loading?.close()
// 例子: 判断不同的HttpErrorCode显示不同的错误信息
if (err.response.status === 404) {
console.log('404的错误~')
}
return err
}
)
}
request<T>(config: HYRequestConfig<T>): Promise<T> {
return new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
// 1.单个请求对请求config的处理
if (config.interceptors?.requestInterceptor) {
config = config.interceptors.requestInterceptor(config)
}
// 2.判断是否需要显示loading
if (config.showLoading === false) {
this.showLoading = config.showLoading
}
this.instance
.request<any, T>(config)
.then((res) => {
// 1.单个请求对数据的处理
if (config.interceptors?.responseInterceptor) {
res = config.interceptors.responseInterceptor(res)
}
// 2.将showLoading设置true, 这样不会影响下一个请求
this.showLoading = DEAFULT_LOADING
// 3.将结果resolve返回出去
resolve(res)
})
.catch((err) => {
// 将showLoading设置true, 这样不会影响下一个请求
this.showLoading = DEAFULT_LOADING
reject(err)
return err
})
})
}
get<T>(config: HYRequestConfig<T>): Promise<T> {
return this.request<T>({ ...config, method: 'GET' })
}
post<T>(config: HYRequestConfig<T>): Promise<T> {
return this.request<T>({ ...config, method: 'POST' })
}
delete<T>(config: HYRequestConfig<T>): Promise<T> {
return this.request<T>({ ...config, method: 'DELETE' })
}
patch<T>(config: HYRequestConfig<T>): Promise<T> {
return this.request<T>({ ...config, method: 'PATCH' })
}
}
export default HYRequest
- type.ts
import type { AxiosRequestConfig, AxiosResponse } from 'axios'
export interface HYRequestInterceptors<T = AxiosResponse> {
requestInterceptor?: (config: AxiosRequestConfig) => AxiosRequestConfig
requestInterceptorCatch?: (error: any) => any
responseInterceptor?: (res: T) => T
responseInterceptorCatch?: (error: any) => any
}
export interface HYRequestConfig<T = AxiosResponse> extends AxiosRequestConfig {
interceptors?: HYRequestInterceptors<T>
showLoading?: boolean
}
# tsconfig.json
{
"compilerOptions": {
// 目标代码(ts -> js(es5/6/7))
"target": "esnext",
// 目标代码需要使用的模块化方案(commonjs require/module.exports/es module import/export)
"module": "esnext",
// 严格一些严格的检查(any)
"strict": true,
// 对jsx进行怎么样的处理
"jsx": "preserve",
// 辅助的导入功能
"importHelpers": true,
// 按照node的方式去解析模块 import "/index.node"
"moduleResolution": "node",
// 跳过一些库的类型检测 (axios -> 类型/ lodash -> @types/lodash / 其他的第三方)
// import { Person } from 'axios'
"skipLibCheck": true,
// export default/module.exports = {}
// es module 和 commonjs
"esModuleInterop": true,
"allowSyntheticDefaultImports": true,
// 要不要生成映射文件(ts -> js)
"sourceMap": true,
// 文件路径在解析时, 基本url
"baseUrl": ".",
// 指定具体要解析使用的类型
"types": ["webpack-env"],
// 路径解析(类似于webpack alias)
"paths": {
"@/*": ["src/*"],
"components/*": ["src/components/*"]
},
// 可以指定在项目中可以使用哪里库的类型(Proxy/Window/Document)
"lib": ["esnext", "dom", "dom.iterable", "scripthost"]
},
"include": [
"src/**/*.ts",
"src/**/*.tsx",
"src/**/*.vue",
"tests/**/*.ts",
"tests/**/*.tsx"
],
"exclude": ["node_modules"]
}
# ts+vue3 获取子组件的实例
- 读取子组件的属性内容:
ref<InstanceType<typeof LoginAccount>>(),因为是没赋值,所以调用子组件的方法时accountRef.value?.loginAction()加问号表示不存在时短路
<template>
<div class="login-panel">
<template >
<span>账号登录</span>
<login-account ref="accountRef" />
</template>
<el-button @click="handleLoginClick"
>立即登录</el-button
>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref } from 'vue'
import LoginAccount from './login-account.vue'
export default defineComponent({
components: {
LoginAccount
},
setup() {
//InstanceType<typeof LoginAccount> === 获取了LoginAccount的实例
const accountRef = ref<InstanceType<typeof LoginAccount>>()
const handleLoginClick = () => {
accountRef.value?.loginAction()
}
return {
handleLoginClick,
accountRef
}
}
})
</script>
当然也可以应用在elementplus的组件上
const formRef = ref<InstanceType<typeof ElForm>>()
const loginAction = () => {
formRef.value?.validate((valid) => {
if (valid) {
console.log('真正执行登录逻辑')
}
})
}
# ts+vue3使用vuex
- IRootState接口
export interface IRootState {
name: string
age: number,
}
- Vuex
import { createStore } from 'vuex'
import login from './login/login'
import { IRootState } from './types'
// createStore可以传入泛型约束state,那么就更好的控制
const store = createStore<IRootState>({
state() {
return {
name: 'coderwhy',
age: 18,
love:'ll'//这边不会报错
}
},
mutations: {
af(state){
// console.log(state.love)
//类型“IRootState”上不存在属性“love”。
}
},
getters: {},
actions: {},
modules: {
login
}
})
export function setupStore() {
store.dispatch('login/loadLocalLogin')
}
export default store
- Login.ts
// 引入Module,ts对vuex的支持还是需要更多的人为操作
import { Module } from 'vuex'
import {
accountLoginRequest,
requestUserInfoById,
requestUserMenusByRoleId
} from '@/service/login/login'
import localCache from '@/utils/cache'
import router from '@/router'
import { IAccount } from '@/service/login/type'
import { ILoginState } from './types'
import { IRootState } from '../types'
// 子模块需要支持自己的state和根模块的state
const loginModule: Module<ILoginState, IRootState> = {
namespaced: true,
state() {
return {
token: '',
userInfo: {},
userMenus: []
}
},
getters: {},
mutations: {
changeToken(state, token: string) {
state.token = token
},
changeUserInfo(state, userInfo: any) {
state.userInfo = userInfo
},
changeUserMenus(state, userMenus: any) {
state.userMenus = userMenus
}
},
actions: {
async accountLoginAction({ commit }, payload: IAccount) {
// 1.实现登录逻辑
const loginResult = await accountLoginRequest(payload)
const { id, token } = loginResult.data
commit('changeToken', token)
localCache.setCache('token', token)
// 2.请求用户信息
const userInfoResult = await requestUserInfoById(id)
const userInfo = userInfoResult.data
commit('changeUserInfo', userInfo)
localCache.setCache('userInfo', userInfo)
// 3.请求用户菜单
const userMenusResult = await requestUserMenusByRoleId(userInfo.role.id)
const userMenus = userMenusResult.data
commit('changeUserMenus', userMenus)
localCache.setCache('userMenus', userMenus)
// 4.跳到首页
router.push('/main')
},
loadLocalLogin({ commit }) {
const token = localCache.getCache('token')
if (token) {
commit('changeToken', token)
}
const userInfo = localCache.getCache('userInfo')
if (userInfo) {
commit('changeUserInfo', userInfo)
}
const userMenus = localCache.getCache('userMenus')
if (userMenus) {
commit('changeUserMenus', userMenus)
}
}
}
}
export default loginModule
# vuex使用useStore的类型检测
- /login/types
export interface ILoginState {
token: string
userInfo: any
userMenus: any
}
- 所有的接口类型交叉之后导出给useStore方法使用
import { ILoginState } from './login/types'
export interface IRootState {
name: string
age: number
}
export interface IRootWithModule {
// 这里可以继续增加其他模块所需要的属性
login: ILoginState
}
//交叉类型进行处理
export type IStoreType = IRootState & IRootWithModule
import { createStore, Store, useStore as useVuexStore } from 'vuex'
import login from './login/login'
import { IRootState, IStoreType } from './types'
const store = createStore<IRootState>({
state() {
return {
name: 'coderwhy',
age: 18
}
},
modules: {
login
}
})
export function setupStore() {
store.dispatch('login/loadLocalLogin')
}
//使用自己的useStore
export function useStore(): Store<IStoreType> {
return useVuexStore()
}
export default store
import { defineComponent, computed } from 'vue'
// 使用自己已经处理过的useStore那样就会增加类型检测了
import { useStore } from '@/store'
setup() {
const store = useStore()
const userMenus = computed(() => store.state.login.userMenus)
return {
userMenus
}
}
# ts+vue3请求接口的封装
export interface IAccount {
name: string
password: string
}
export interface ILoginResult {
id: number
name: string
token: string
}
export interface IDataType<T = any> {
code: number
data: T
}
import hyRequest from '../index'
import { IAccount, IDataType, ILoginResult } from './type'
enum LoginAPI {
AccountLogin = '/login',
LoginUserInfo = '/users/', // 用法: /users/1
}
export function accountLoginRequest(account: IAccount) {
//泛型嵌套
return hyRequest.post<IDataType<ILoginResult>>({
url: LoginAPI.AccountLogin,
data: account
})
}
export function requestUserInfoById(id: number) {
return hyRequest.get<IDataType>({
url: LoginAPI.LoginUserInfo + id,
showLoading: false
})
}
//post<IDataType<ILoginResult>>这里的T就是上面get/post后跟的T,就是为了约束返回值data的类型
post<T>(config: HYRequestConfig<T>): Promise<T> {
return this.request<T>({ ...config, method: 'POST' })
}
# ts+vue3 PropType: props增加具体对象数组限制
利用propType,它可以通过泛型进行对父组件传过来的格式进行约束。
import { defineComponent, PropType } from 'vue'
type IFormType = 'input' | 'password' | 'select' | 'datepicker'
export interface IFormItem {
type: IFormType
label: string
rules?: any[]
placeholder?: any
// 针对select
options?: any[]
// 针对特殊的属性
otherOptions?: any
}
export default defineComponent({
props: {
formItems: {
type: Array as PropType<IFormItem[]>,
default: () => []
}
},
setup() {
return {}
}
})
# ts+vue3 table封装
export const contentTableConfig = {
title: '用户列表',
propList: [
{ prop: 'name', label: '用户名', minWidth: '100' },
{ prop: 'realname', label: '真实姓名', minWidth: '100' },
{ prop: 'cellphone', label: '手机号码', minWidth: '100' },
{ prop: 'enable', label: '状态', minWidth: '100', slotName: 'status' },
{
prop: 'createAt',
label: '创建时间',
minWidth: '250',
slotName: 'createAt'
},
{
prop: 'updateAt',
label: '更新时间',
minWidth: '250',
slotName: 'updateAt'
},
{ label: '操作', minWidth: '120', slotName: 'handler' }
],
showIndexColumn: true,
showSelectColumn: true
}
<template>
<div class="hy-table">
<el-table
:data="listData"
border
style="width: 100%"
@selection-change="handleSelectionChange"
>
<el-table-column
v-if="showSelectColumn"
type="selection"
align="center"
width="60"
></el-table-column>
<el-table-column
v-if="showIndexColumn"
type="index"
label="序号"
align="center"
width="80"
></el-table-column>
<template v-for="propItem in propList" :key="propItem.prop">
<el-table-column v-bind="propItem" align="center">
<template #default="scope">
<slot :name="propItem.slotName" :row="scope.row">
{{ scope.row[propItem.prop] }}
</slot>
</template>
</el-table-column>
</template>
</el-table>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
props: {
title: {
type: String,
default: ''
},
listData: {
type: Array,
required: true
},
propList: {
type: Array,
required: true
},
showIndexColumn: {
type: Boolean,
default: false
},
showSelectColumn: {
type: Boolean,
default: false
}
},
emits: ['selectionChange'],
setup(props, { emit }) {
const handleSelectionChange = (value: any) => {
emit('selectionChange', value)
}
return {
handleSelectionChange
}
}
})
</script>
<hy-table :listData="dataList" v-bind="contentTableConfig">
<!--列中的插槽 -->
<template #status="scope">
<el-button
plain
size="mini"
:type="scope.row.enable ? 'success' : 'danger'"
>
{{ scope.row.enable ? '启用' : '禁用' }}
</el-button>
</template>
<template #createAt="scope">
<span>{{ $filters.formatTime(scope.row.createAt) }}</span>
</template>
<template #updateAt="scope">
<span>{{ $filters.formatTime(scope.row.updateAt) }}</span>
</template>
<template #handler>
<div class="handle-btns">
<el-button icon="el-icon-edit" size="mini" type="text"
>编辑</el-button
>
<el-button icon="el-icon-delete" size="mini" type="text"
>删除</el-button
>
</div>
</template>
</hy-table>
props: {
contentTableConfig: {
type: Object,
require: true
}
},
# ts+vue3 对象表单的双向绑定处理
# 子组件v-model变化通知父组件更新
+ 子组件
<template>
<el-form :label-width="labelWidth">
<el-input
:placeholder="item.placeholder"
v-bind="item.otherOptions"
:show-password="item.type === 'password'"
v-model="formData[`${item.field}`]"
/>
</el-form>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, PropType, ref, watch, computed } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
props: {
modelValue: {
type: Object,
required: true
}
},
setup(props, { emit }) {
//因为是浅拷贝,所以当改到formData.value.key,这里还是可以动态变化
const formData = ref({ ...props.modelValue })
watch(
formData,
(newValue) => {
console.log(newValue)
emit('update:modelValue', newValue)
},
{
deep: true
}
)
return {
formData
}
}
})
</script>
+ 父组件
<div class="page-search">
<hy-form v-bind="searchFormConfig" v-model="formData">
<template #header>
<h1 class="header">高级检索</h1>
</template>
<template #footer>
<div class="handle-btns">
<el-button icon="el-icon-refresh" @click="handleResetClick"
>重置</el-button
>
<el-button type="primary" icon="el-icon-search">搜索</el-button>
</div>
</template>
</hy-form>
</div>
const formOriginData: any = {}
for (const item of formItems) {
formOriginData[item.field] = ''
}
//父组件接收到重置表单的命令,清空原表单的数据
const handleResetClick = () => {
for (const key in formOriginData) {
formData.value[`${key}`] = formOriginData[key]
}
}
- 另一种模式
<!-- 父组件 -->
<template>
<div class="page-search">
<hy-form v-bind="searchFormConfig" v-model="formData">
<template #footer>
<div class="handle-btns">
<el-button icon="el-icon-refresh" @click="handleResetClick"
>重置</el-button
>
</div>
</template>
</hy-form>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, ref } from 'vue'
import HyForm from '@/base-ui/form'
export default defineComponent({
props: {
searchFormConfig: {
type: Object,
reuqired: true
}
},
components: {
HyForm
},
emits: ['resetBtnClick', 'queryBtnClick'],
setup(props, { emit }) {
// 双向绑定的属性应该是由配置文件的field来决定
// 1.优化一: formData中的属性应该动态来决定
const formItems = props.searchFormConfig?.formItems ?? []
const formOriginData: any = {}
for (const item of formItems) {
formOriginData[item.field] = ''
}
const formData = ref(formOriginData)
// 2.优化二: 当用户点击重置
const handleResetClick = () => {
formData.value = formOriginData
}
return {
formData,
handleResetClick,
handleQueryClick
}
}
})
</script>
- 子组件使用modelValue
<template>
<div class="hy-form">
<el-form :label-width="labelWidth">
<el-input
:placeholder="item.placeholder"
v-bind="item.otherOptions"
:show-password="item.type === 'password'"
:model-value="modelValue[`${item.field}`]"
@update:modelValue="handleValueChange($event, item.field)"
/>
</el-form>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, PropType } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
props: {
modelValue: {
type: Object,
required: true
},
},
emits: ['update:modelValue'],
setup(props, { emit }) {
const handleValueChange = (value: any, field: string) => {
emit('update:modelValue', { ...props.modelValue, [field]: value })
}
return {
handleValueChange
}
}
})
</script>
← 封装elementplus threejs →