# vue.sync
.sync 相当于对一个props进行双向绑定,也是一个语法糖
<!--语法糖.sync,vue3不支持这种语法了-->
<my-component :value.sync="msg" />
<!--编译后的写法,这种写法可以继续在vue3中使用,相当于v-model:value-->
<my-component
:value="msg"
@update:value="(val) => msg = val"
/>
# 案例
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue-03</title>
<!-- 引入Vue -->
<link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.16/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" style="margin-top: 12px;">
<div id="demo" class="row">
{{ say }}
<br />
<my-input :value.sync="say"></my-input>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
say: "123"
},
components: {
"my-input": {
props: ['value'],
template: "<div><input v-bind:value='value' v-on:input='change1' />{{value}}</div>",
watch: {
value: function(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log('子组件value新旧值' + newValue + '/' + oldValue);
}
},
methods: {
change1: function(e) {
var v = e.target.value
this.$emit('update:value', v)
},
}
}
},
watch: {
say: function(n, o) {
console.log('父组件新旧值' + n + '-' + o)
}
},
})
</script>
</body>
props的.sync在vue3中被移除
替代方案:
<ChildComponent v-model:title="pageTitle" />
<!-- 是以下的简写: -->
<ChildComponent :title="pageTitle" @update:title="pageTitle = $event" />
+ v-model:show="valueChild" => show作为props传给子组件
+ 子组件调用update:show=>this.$emit('update:show', false); 通知父组件
+ 父组件直接valueChild = 传递过来的值;修改了show的值,子组件进行响应的变化
- 父组件
<template>
<div>
<Children1 v-model:show="valueChild" style="padding: 30px 20px 30px 5px;border:1px solid #ddd;margin-bottom: 10px;"/>
<button @click="changeValue">toggle</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import { ref } from 'vue'
import Children1 from './com/Children1.vue'
export default {
data(){
return{
valueChild:true,
}
},
methods:{
changeValue(){
this.valueChild = !this.valueChild
}
},
components:{
Children1
},
}
</script>
- 子组件
<template>
<div v-if="show">
<p>默认初始值是{{show}},所以是显示的</p>
<button @click.stop="closeDiv">关闭</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
props:['show'],
methods: {
closeDiv() {
this.$emit('update:show', false); //触发 input 事件,并传入新值
}
}
}
</script>
# v-model
# v-model的修饰符
修饰符 lazy, number, trim
v-model其实只是语法糖,在input标签内写上v-model后,实际上在vue内会编译为:
<!--v-model写法-->
<input type="text" v-model="value">
<!--编译后的写法-->
<input type="text"
:value="value"
@input="value = $event.target.value"
>
问题来了,如果这个input是个组件(暂且叫input-component吧),想在父组件中使用input-component这个组件,我们能直接使用v-model进行双向绑定吗?
答案是:很遗憾,不能,因为v-model只是一个语法糖,他的原本写法上面已经提过,绑定value值,监听input事件,通过event拿到value并赋值给value。
那么要怎么做才能在组件上使用v-model呢? 很简单,当input-component触发input事件时,让他发布一个input事件,并带上$event.target.value,在父组件上,我们用v-model监听这个input事件,就能实现了
this.$emit('input',e.target.value)触发input事件怎么理解
<!--子组件-->
<input type="text"
:value="value"
@input="$emit('input', $event.target.value);"
>
<!--父组件-->
<input-component v-model="value">
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>vue-10</title>
<!-- 引入Vue -->
<link href="https://cdn.bootcss.com/bootstrap/4.1.1/css/bootstrap.min.css" rel="stylesheet">
<script src="https://cdn.bootcss.com/vue/2.5.16/vue.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div class="container" style="margin-top: 12px;">
<div id="demo" class="row">
{{ say }}
<br />
<my-input v-model="say"></my-input>
</div>
</div>
<script>
new Vue({
el: '#demo',
data: {
say: "123"
},
components: {
"my-input": {
props: ['value'],
template: "<div><input v-bind:value='value' v-on:input='change' />{{value}}</div>",
watch: {
value: function(newValue, oldValue) {
console.log('子组件value新旧值' + newValue + '/' + oldValue);
}
},
methods: {
change: function(e) {
this.$emit('input', e.target.value)
}
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
# v-model 自定义组件checkbox使用方法
- 子组件T1, 定义一个model用来接受属性和调用的方法
<template>
<div>
<input type="checkbox" :checked='checked' @change="changeval">
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props:{
checked:Boolean
},
model:{
prop:'checked',
event:'change'
},
methods:{
changeval(e){
console.log(e.target.checked)
this.$emit('change',e.target.checked)
}
}
}
</script>
<style>
</style>
- 父组件
<template>
<div class="home">
<T1 v-model='checked'/>
{{checked}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import T1 from '@/components/T1.vue'
export default {
name: 'Home',
components: {
T1
},
data(){
return {
checked:false
}
}
}
</script>
# vue3 v-model的改变

<!-- input上使用v-model -->
<input v-model="message">
<!-- 等价于 -->
<input :value="message" @input="message = $event.target.value">
<!-- 组件上使用v-model -->
<hy-input v-model="message"></hy-input>
<!-- 等价于 -->
<hy-input :modelValue="message" @update:model-value="message = $event"></hy-input>
依然希望在组件内部按照双向绑定的做法去完成,应该如何操作呢?可以使用计算属性的setter和getter来完成。
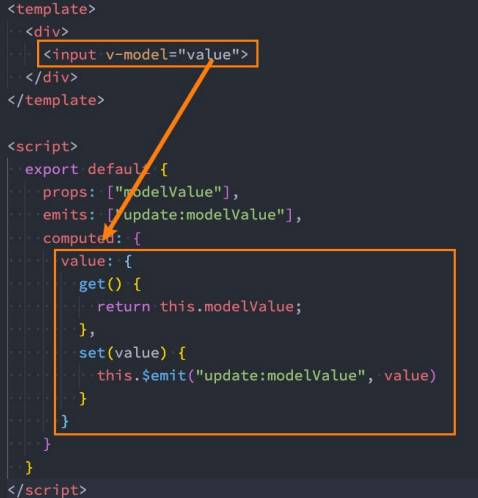
<template>
<div class="validate-input-container pb-3">
<input
v-model="inputRef.val"
v-bind="$attrs"
>
</div>
</template>
<script lang="ts">
import { defineComponent, reactive, PropType, computed } from 'vue'
export default defineComponent({
props: {
modelValue: String,
},
setup(props, context) {
const inputRef = reactive({
val: computed({
get: () => props.modelValue || '',
set: val => {
context.emit('update:modelValue', val)
}
}),
})
return {
inputRef
}
}
})
</script>
v-model 可以使用在双向绑定的场景,此时,v-model的用法有限制
- 传递给子组件props名字固定为modelValue,更新值得事件需要$emit发送'update:modelValue'
- 如果不想使用modelValue,需要改成v-model:xx='ss',props=>xx ,发送事件为update:xx
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>lesson 18</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return { count: 1 }
},
template: `
<counter v-model="count" />
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: ['modelValue'],
methods: {
handleClick() {
this.$emit('update:modelValue', this.modelValue + 3);
}
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</html>
自定义插件如果需要监听多个数据的变动,可以同时绑定多个v-model,需要自主命名来区分. v-model:app1 ,v-model:app2,同时还可以添加自定义修饰符
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>lesson 19</title>
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue@next"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
<script>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
count: 'a',
}
},
template: `
<counter v-model.uppercase="count" />
`
});
app.component('counter', {
props: {
'modelValue': String,
'modelModifiers': {
default: ()=> ({})
}
//modelModifiers固定写法
},
methods: {
handleClick() {
let newValue = this.modelValue + 'b';
if(this.modelModifiers.uppercase) {
newValue = newValue.toUpperCase();
}
this.$emit('update:modelValue', newValue);
},
},
template: `
<div @click="handleClick">{{modelValue}}</div>
`
});
const vm = app.mount('#root');
</script>
</html>
# vue3 v-model自定义修饰符
当我们学习表单输入绑定时,我们看到 v-model 有内置修饰符——.trim、.number 和 .lazy。但是,在某些情况下,你可能还需要添加自己的自定义修饰符。
让我们创建一个示例自定义修饰符 capitalize,它将 v-model 绑定提供的字符串的第一个字母大写。
添加到组件 v-model 的修饰符将通过 modelModifiers prop 提供给组件。在下面的示例中,我们创建了一个组件,其中包含默认为空对象的 modelModifiers prop。
请注意,当组件的 created 生命周期钩子触发时,modelModifiers prop 会包含 capitalize,且其值为 true——因为 capitalize 被设置在了写为 v-model.capitalize="myText" 的 v-model 绑定上。
<my-component v-model.capitalize="myText"></my-component>
app.component('my-component', {
props: {
modelValue: String,
modelModifiers: {
default: () => ({xxx:false||true})//
//比如在父组件v-model如果没有定义这个自定义修饰符,可以在这里使用默认值。根据实际情况去设置
// v-model.capitalize =>v-model 那就取这里的默认值了
}
},
emits: ['update:modelValue'],
template: `
<input type="text"
:value="modelValue"
@input="$emit('update:modelValue', $event.target.value)">
`,
created() {
console.log(this.modelModifiers) // { capitalize: true }
}
})
现在我们已经设置了 prop,我们可以检查 modelModifiers 对象键并编写一个处理器来更改发出的值。在下面的代码中,每当 <input/> 元素触发 input 事件时,我们都将字符串大写。
<div id="app">
<my-component v-model.capitalize="myText"></my-component>
{{ myText }}
</div>
const app = Vue.createApp({
data() {
return {
myText: ''
}
}
})
app.component('my-component', {
props: {
modelValue: String,
modelModifiers: {
default: () => ({})
}
},
emits: ['update:modelValue'],
methods: {
emitValue(e) {
let value = e.target.value
if (this.modelModifiers.capitalize) {
value = value.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + value.slice(1)
}
this.$emit('update:modelValue', value)
}
},
template: `<input
type="text"
:value="modelValue"
@input="emitValue">`
})
app.mount('#app')
对于带参数的 v-model 绑定,生成的 prop 名称将为 arg + "Modifiers":
<my-component v-model:description.capitalize="myText"></my-component>
app.component('my-component', {
props: ['description', 'descriptionModifiers'],
emits: ['update:description'],
template: `
<input type="text"
:value="description"
@input="$emit('update:description', $event.target.value)">
`,
created() {
console.log(this.descriptionModifiers) // { capitalize: true }
}
})
# vue2和vue3的v-model的总结
- 2.x 中 v-model 语法糖底层使用的是 :value 和 emit(‘input’), 绑定属性值是 value
- 3.0 中可以绑定一个自定义值,支持统一组件绑定多个 v-model,v-model:firstName=“firstName”, :value=“firstName” 和 @input="$emit(‘update:firstName’, $event.target.value)" 添加自定义修饰符 v-model.capitalize
- app.vue
<template>
<div id="app">
<h1>Vue3中v-model的变化</h1>
<input type="text" v-model="name"/>
<p>{{ name }}</p>
<!-- Vue2的写法 -->
<!-- v-model实际上就是:value和@input的语法糖 -->
<!-- 双向绑定多个属性的时候可以使用.sync关键字 -->
<CustomInput v-model="age" :name.sync="name"/>
<!-- Vue3的写法 -->
<CustomInput v-model:age="age" v-model:name="name"/>
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CustomInput from "../components/CustomInput.vue";
export default {
name: "App",
components: {
CustomInput
},
data() {
return {
name: "你好",
age: 20,
}
},
}
</script>
- CustomInput.vue
<template>
<div class="custom-input">
<h1>自定义的input</h1>
<!-- Vue2的写法 -->
<input type="text" :value="value" @input="onInput" />
<input type="text" :value="name" @input="onNameInput" />
<!-- Vue3的写法 -->
<input type="text" :value="age" @input="onInput" />
<input type="text" :value="name" @input="onNameInput" />
</div>
</template>
<script>
import CustomInput from "../components/CustomInput.vue";
export default {
// Vue2的写法
props: ["value", "name"],
// Vue3的写法,直接接收绑定的参数
props: ["age", "name"],
// Vue3双向绑定单个属性时,可以使用modelValue来接收参数并更新,对应的触发事件为update:modelValue
props: ["modelValue"],
methods: {
onInput(e) {
// Vue2的写法
// 触发的事件只能是input
// e.target.value是字符串需要转换成数字
this.$emit("input", parseInt(e.target.value));
// Vue3的写法
this.$emit("update:age", e.target.value);
},
onNameInput(e) {
// 只能用update
this.$emit("update:name", e.target.value);
},
},
}
</script>
# 2022年4月27日整理(vue2)
- v-model是语法糖,
可以用在自定义组件中,会被解析为value和@input事件 - 如果子组件中完全没用到input,select,textarea,checkbox也是可以用v-model,如例myinput.vue
- 默认子组件接受value,触发事件input,但是可以通过子组件中的
model修改props中的名字和事件触发的名字,如myinput2.vue - (如果不是用model,那么参数仍然是value,触发条件仍然是input事件)
- 注意checkbox修改的值是
e.target.checked,不是e.target.value
<template>
<div>
<input type="text" v-model='t1'/>
<myinput type="text" v-model='t2'/>
t2:{{t2}}
<br>
<myinput1 v-model='t3' />
t3:{{t3}}
<br>
<myinput2 v-model='t4'/>
t4:{{t4}}
</div>
</template>
<script>
import myinput from './myinput.vue'
import myinput1 from './myinput1.vue'
import myinput2 from './myinput2.vue'
export default{
data(){
return {
t1:10,
t2:20,
t3:30,
t4:true
}
},
components:{
myinput,
myinput1,
myinput2
},
methods:{
}
}
</script>
- myinput.vue
<template>
<div>
<p>my input</p>
{{value}}
<button @click='add'>+</button>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default {
props:{
value:Number,
},
methods:{
add(){
this.$emit('input',this.value+5)
}
}
}
</script>
- myinput1.vue
<template>
<div>
<select name="" :value='value' @change='changefun'>
<option :value="item" v-for='item in arr' :key='item' >{{item}}</option>
</select>
</div>
</template>
<script>
export default{
props:['value'],
data(){
return{
arr:[5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40]
}
},
methods:{
changefun(e){
console.log(e.target.value)
this.$emit('input',e.target.value)
}
}
}
</script>
- myinput2.vue
<template>
<input type="checkbox" :checked="checked" @change='fun'/>
</template>
<script>
export default{
props:['checked'],
model:{
prop:'checked',
event:'change'
},
methods:{
fun(e){
this.$emit('change',e.target.checked)
}
}
}
</script>